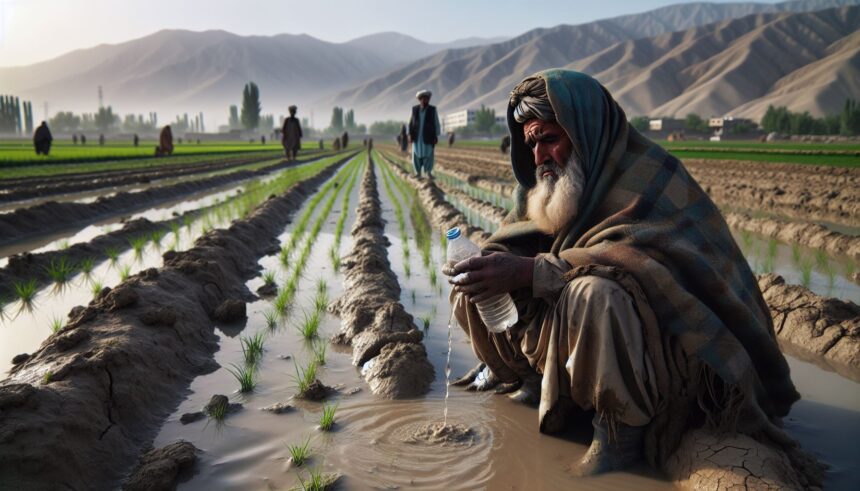
Afghanistan is a landlocked country in South Asia, bordered by Pakistan, Iran, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and China. Its population is about 38 million, most of whom depend on agriculture and natural resources for their livelihoods. Afghanistan has also been affected by decades of conflict, instability, and poverty, undermining its social and economic development.
Amidst these formidable challenges, Afghanistan finds itself in a precarious position. It is one of the 10 countries most vulnerable to climate change and among the few least prepared for such a situation, as per the Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative (ND-GAIN) index. The threat of climate change looms large, not just over the lives and well-being of millions of Afghans, but also over the stability and security of the country and the region. In this document, we will delve into Afghanistan’s impacts, vulnerabilities, and adaptation strategies in the face of this urgent global crisis.
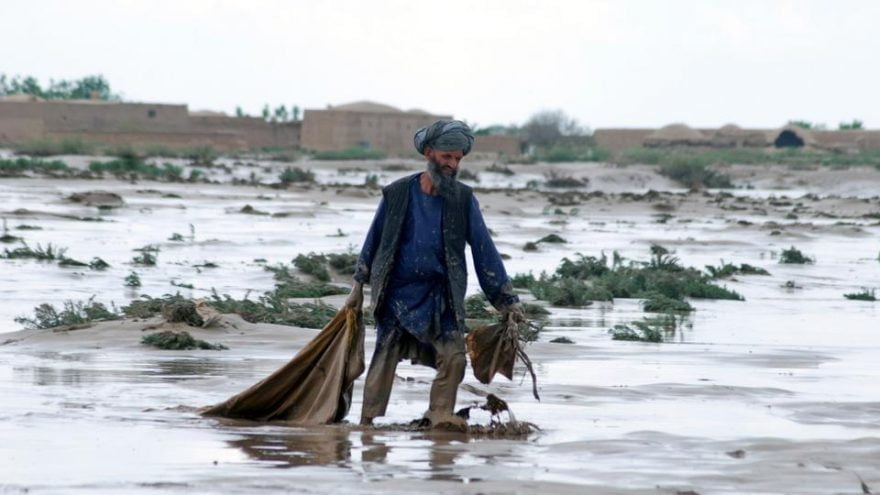

Impacts of Climate Change on Afghanistan
Climate change is expected to have multiple and complex effects on Afghanistan, varying across regions and sectors. Some of the main impacts are:
- One of the most pressing issues is the Increase in temperature and evaporation. Afghanistan’s average temperature has risen by about 1.8°C since 1950, which is set to continue. This will accelerate the evaporation rate and reduce soil moisture, directly impacting crop yields and water availability, which are the lifeblood of most Afghans’ livelihoods.
- Reduced precipitation and snowpack: Afghanistan receives most of its precipitation in the form of snowfall in the winter, which feeds the rivers and groundwater sources in the spring and summer. However, climate change is likely to reduce the amount and reliability of snowfall and the duration and extent of snow cover, leading to less water for irrigation, drinking, and hydropower.
- Another significant impact is the projected Increase in the frequency and intensity of droughts and floods. This will lead to more erratic and unpredictable rainfall patterns, resulting in more frequent and severe droughts and floods. The consequences are dire: droughts can lead to crop failures, food insecurity, malnutrition, and displacement, while floods can cause extensive damage to infrastructure, property, and lives and increase the risk of waterborne diseases and landmines.
- Increased desertification and land degradation: Climate change will exacerbate the existing problems of desertification and land degradation in Afghanistan, which are caused by factors such as overgrazing, deforestation, erosion, salinization, and mining. These processes can reduce the productivity and biodiversity of the land and increase the population’s vulnerability to natural disasters and conflicts.
- Increased glacier melt and glacial lake outburst floods: Afghanistan has about 2,000 glaciers, which are essential water sources for the country and the region. However, these glaciers are melting at an alarming rate due to climate change, which can negatively affect the country’s water balance and hydrology. Moreover, the melting of glaciers can create glacial lakes, which can burst and cause devastating floods downstream.
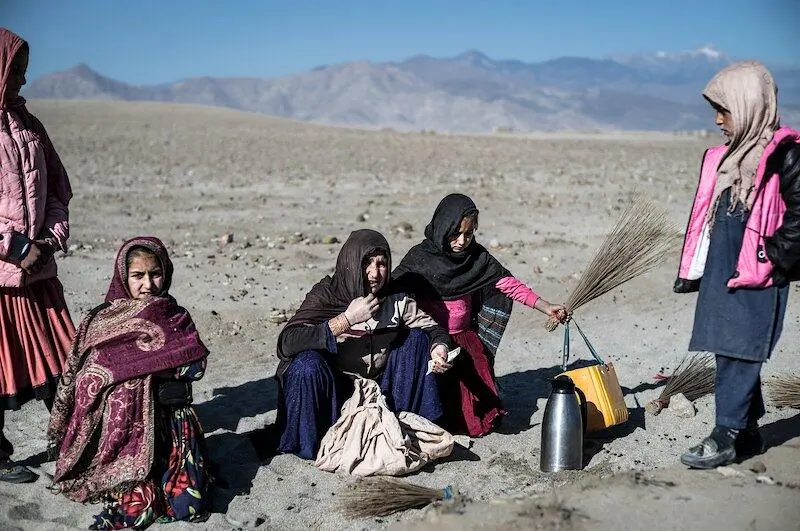

Vulnerabilities of Afghanistan to Climate Change
The impacts of climate change on Afghanistan will not be evenly distributed or experienced by all segments of the society. Some of the factors that make Afghanistan more vulnerable to climate change are:
- Low adaptive capacity: Afghanistan has a low adaptive capacity to cope with and recover from the effects of climate change due to its low level of human development, weak governance, limited institutional and technical capacities, inadequate infrastructure, and high dependence on external aid.
- High exposure and sensitivity: Afghanistan is highly exposed to and sensitive to climate change due to its geographic location, topography, climate, and ecology. It is in a region prone to extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, heat waves, and cold snaps. It also has a diverse and fragile ecosystem, home to many endemic and endangered species.
- High poverty and inequality: Afghanistan has a high poverty and inequality rate, which affects the ability of the people to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change. According to the World Bank, about 55% of the population lives below the national poverty line and about 20% lives in extreme poverty. Poverty and inequality are also linked to other social issues, such as illiteracy, unemployment, gender discrimination, and lack of access to essential services.
- High conflict and insecurity: Afghanistan has a high conflict and insecurity situation, which hampers the efforts to address the challenges of climate change. The country has been in a state of war for more than 40 years, which has resulted in widespread violence, displacement, human rights violations, and environmental degradation. Conflict and insecurity also undermine the trust and cooperation among stakeholders, such as the government, civil society, and the international community.
Adaptation Strategies for Afghanistan
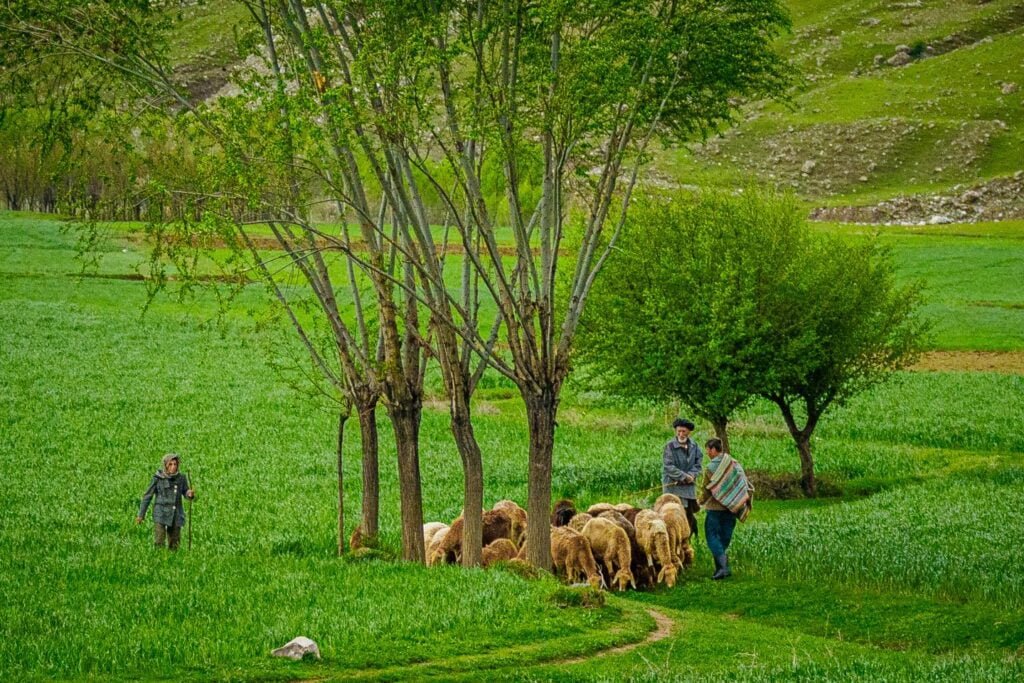

Despite the daunting challenges, Afghanistan has taken some steps to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change, with the support of various national and international actors. Some of the adaptation strategies that have been implemented or proposed are:
- Improving water management and conservation: This includes building water harvesting and storage structures, rehabilitating irrigation systems, promoting efficient water use and allocation, enhancing groundwater recharge, and developing early warning systems for droughts and floods.
- Enhancing food security and agricultural resilience: This includes measures such as introducing drought-tolerant and high-yielding crop varieties, diversifying crop and livestock production, improving soil and pest management, promoting agroforestry and rangeland restoration, and strengthening food distribution and safety nets.
- Reducing disaster risk and building community resilience: This includes improving disaster preparedness and response, strengthening disaster risk governance and coordination, raising awareness and education on climate change and disaster risk reduction, and supporting community-based adaptation and local coping strategies.
- Addressing the root causes and drivers of vulnerability: Reducing poverty and inequality, improving governance and rule of law, enhancing human rights and gender equality, promoting peace and security, and fostering regional and international cooperation.
Conclusion
Afghanistan is a country that faces multiple and interrelated challenges, which are exacerbated by the effects of climate change. Climate change poses a severe threat to the lives and well-being of millions of Afghans, as well as to the stability and security of the country and the region. However, Afghanistan also has the potential and the opportunity to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change by implementing various strategies that can enhance its resilience and sustainability. Afghanistan needs the support and collaboration of all stakeholders, including the government, civil society, and the international community.